A pathway coordinated by DELE1 relays mitochondrial stress to the cytosol
March 4, 2020·,,, ,,,,,·
0 min read
,,,,,·
0 min read
Evelyn Fessler
Eva-Maria Eckl
Sabine Schmitt
Igor Alves Mancilla
Matthias Meyer-Bender
Monika Hanf
Julia Philippou-Massier
Stefan Krebs
Hans Zischka
Lucas Jae
Abstract
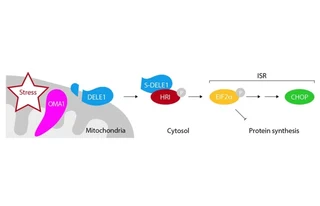
Mitochondrial fidelity is tightly linked to overall cellular homeostasis and is compromised in ageing and various pathologies. Mitochondrial malfunction needs to be relayed to the cytosol, where an integrated stress response is triggered by the phosphorylation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2α (eIF2α) in mammalian cells. eIF2α phosphorylation is mediated by the four eIF2α kinases GCN2, HRI, PERK and PKR, which are activated by diverse types of cellular stress. However, the machinery that communicates mitochondrial perturbation to the cytosol to trigger the integrated stress response remains unknown.
Here we combine genome engineering and haploid genetics to unbiasedly identify genes that affect the induction of C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP), a key factor in the integrated stress response. We show that the mitochondrial protease OMA1 and the poorly characterized protein DELE1, together with HRI, constitute the missing pathway that is triggered by mitochondrial stress. Mechanistically, stress-induced activation of OMA1 causes DELE1 to be cleaved into a short form that accumulates in the cytosol, where it binds to and activates HRI via its C-terminal portion. Obstruction of this pathway can be beneficial or adverse depending on the type of mitochondrial perturbation. In addition to the core pathway components, our comparative genetic screening strategy identifies a suite of additional regulators. Together, these findings could be used to inform future strategies to modulate the cellular response to mitochondrial dysfunction in the context of human disease.
Here we combine genome engineering and haploid genetics to unbiasedly identify genes that affect the induction of C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP), a key factor in the integrated stress response. We show that the mitochondrial protease OMA1 and the poorly characterized protein DELE1, together with HRI, constitute the missing pathway that is triggered by mitochondrial stress. Mechanistically, stress-induced activation of OMA1 causes DELE1 to be cleaved into a short form that accumulates in the cytosol, where it binds to and activates HRI via its C-terminal portion. Obstruction of this pathway can be beneficial or adverse depending on the type of mitochondrial perturbation. In addition to the core pathway components, our comparative genetic screening strategy identifies a suite of additional regulators. Together, these findings could be used to inform future strategies to modulate the cellular response to mitochondrial dysfunction in the context of human disease.
Type
Publication
Nature
Authors
Authors
Authors
Authors

Authors
Matthias Meyer-Bender
(he/him)
Bioinformatician
I am a PhD candidate at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in the group of Wolfgang Huber. My current work focuses on developing open-source software for the processing and analysis of large-scale spatial omics datasets (spatialproteomics). I am passionate about applying computational methods, including machine learning and AI, to answer questions of biomedical relevance. Previously, I studied bioinformatics at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) and Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich (LMU). I also contribute to open-source projects such as scverse.
Authors
Authors
Authors
Authors
Authors